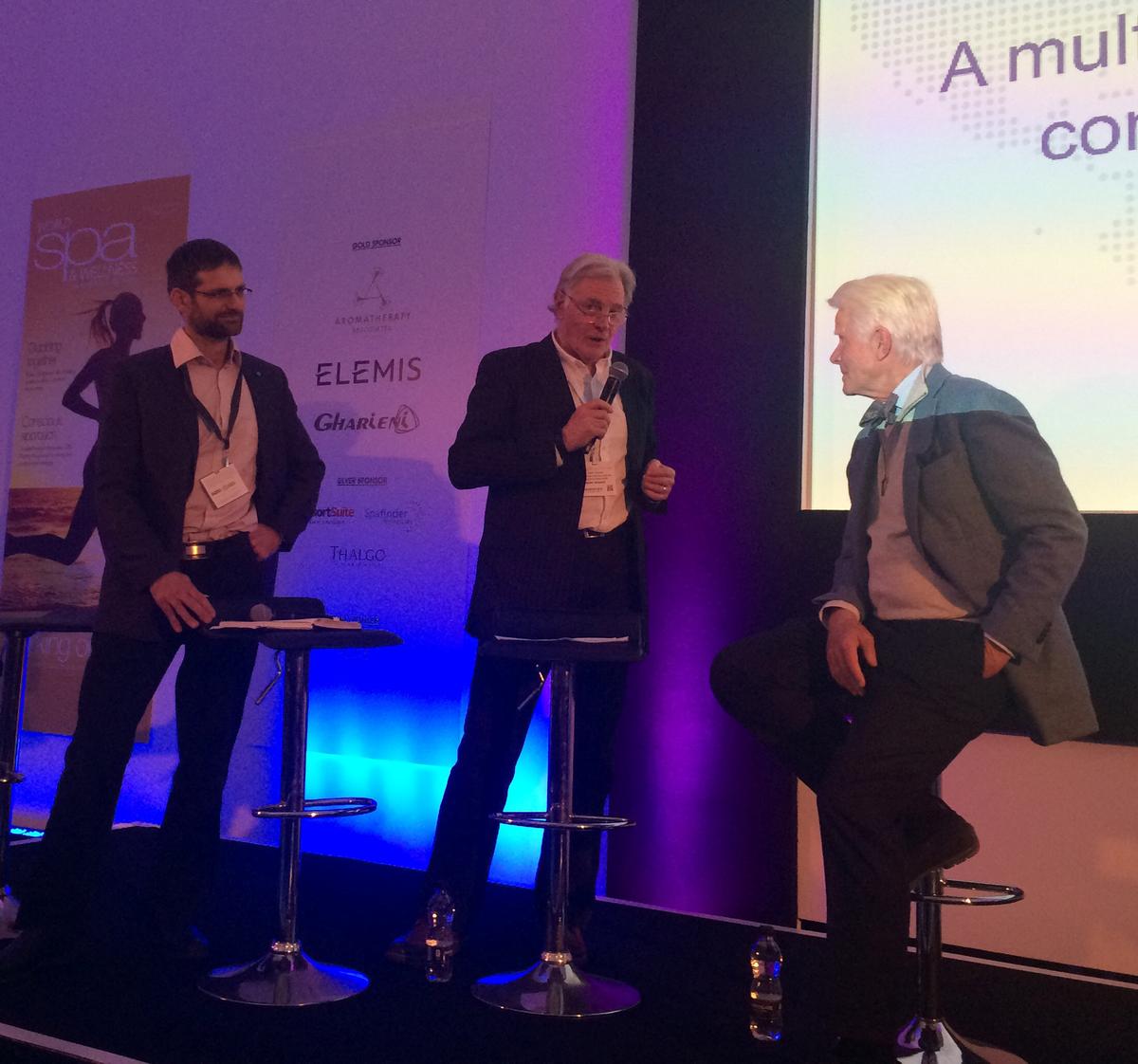
Mia Kyricos, founder of strategic advisory firm Kyricos & Associates, told an audience at the World Spa & Wellness Convention in London that wellness communities grew by 19 per cent from 2013 to 2015, and are worth an estimated US$29bn (€27.5bn, £23.6bn) in Europe and US$48bn (€45.6bn, £39.1bn) in North America.
Kyricos moderated a panel on wellness communities that also included Steve Nygren, president of Serenbe wellness community near Atlanta, US; Ben H Gill, international technical manager for One Planet Communities Programme; and Professor Terry Stevens, founder and managing director of Stevens & Associates.
Stevens said that many of the things we’re looking for in today’s wellness communities are things we took for granted a few generations ago, when we often lived in smaller communities that offered social connections.
“Somewhere in this model of a traditional community, we find what it is we’re looking for on this new horizon,” he said.
Nygren agreed, and said that new regulations have often moved us away from this model.
“The way we lived in our villages 80 or 100 years ago, we had all that we desired,” he said.
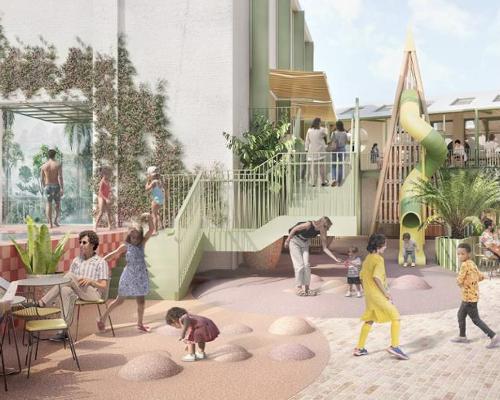
Things like local agriculture, social connections, and the ability to spend time in nature are all an important part of life at Serenbe and many other wellness communities, which have been defined by the Global Wellness Institute’s initiative on the subject as “communities and buildings proactively developed with the holistic health of its residents, guests, environment – both natural and built – and local community in mind.”
At Bedzed, a community in south London developed by One Planet, residents know on average more than 20 neighbours by name, said Gill, compared to a national average of eight. This points to a more socially connected community – something that’s proven good for mental wellness.
Stevens said that in order to succeed, wellness communities need to be geographically compact, coherent, and competently managed. “You’re not going to achieve the goals unless there’s competent management,” he said.
Stevens further detailed that several paradigm shifts are helping to fuel the growth of and interest in wellness communities: first, a move toward values not value, where experiences and what something stands for is more important to today’s consumer than what it costs; second, “the rich are buying less but spending more,” said Stevens; and third, “the public sector are recognising that they have to be facilitators but not doers.”
Gill echoed Stevens’ point about buying less but spending more. “Quality can mean different things,” he said. At the One Brighton community in south England, for instance, the quality of the buildings and fixtures is higher, but there is no car park – something those buying into a the community are happy to do without in their quest for well living.
“Millennials and Baby Boomers are both starting to gravitate towards urban environments with a walking grid,” said Nygren. “They want to connect to nature and to each other.”
Looking back at the village model from 100 years ago shows another change, said Stevens: every village had a doctor, who was interested in preventing sickness as much as treating it.
“We have turned our doctors into institutions,” he said. “And there’s a huge opportunity for spas to move into this.”
The panel agreed that wellness communities should include spas, and that they should become part of the culture of vitality and living.
“You have a great opportunity to not just exist at the side of things, but to live at the heart of the community,” said Kyricos.